Molybdenum

Molybdenum plays an important role in the alloys it produces with steel due to its strong carbide forming feature. Having a high melting point (2610 ° C), molybdenum also has high thermal conductivity and the lowest heat expansion among pure metals.
Molybdenum is an alloy material used in special steels, pig iron, nickel, cobalt and titanium-based alloys. Alloys containing molybdenum are widely used in the production of stainless steel, tubular and tubular tools, super heaters, steel resistances, petroleum products and chemical processes. It is chemically used in molybdenum fabric dyeing, which has a wide range of uses, to obtain alcohol and formaldehyde. In addition, magnet alloys, cast carbides are used in the manufacture of water and gas impermeable materials, and have been added to oils and greases in recent years due to their friction reducing properties.

According to the 2023 data published in the USGS 2024 report, the world's molybdenum reserves are 15 million tons, and China ranks first in the world's molybdenum reserve ranking with 40%. According to the 2023 production data in the USGS report, 260 thousand tons of molybdenum were produced in the world and the largest molybdenum producer is China, with a production of 110,000 tons, accounting for approximately 40% of world production.

Molybdenum commonly shows five types of bedding. These are porphyry and disseminated deposits, contact metaformic deposits, quartz veins, pegmatite and aplite dykes and bedded beds in sedimentary rocks. More than 95% of the molybdenum production in the world is made of por molybdenum and porry copper molybdenum deposits.
The most suitable mining method for molybdenum, which can be produced with both underground and aboveground operating methods, is determined by evaluating the size, shape, grade and depth of mineralization. Worldwide, 55% of molybdenum mining is carried out as underground and 45% as open pit.
In its main application in steels and cast irons, there are few substitutes that can be used instead of molybdenum. In fact, due to the availability and versatility of molybdenum, new materials have been attempted to be developed by the industry to utilize alloy properties. Potential substitutes include boron, chromium, niobium (colombium) and vanadium in alloy steels; tungsten in tool steels; There are graphite, tantalum and tungsten for refractory materials in high temperature electric furnaces.
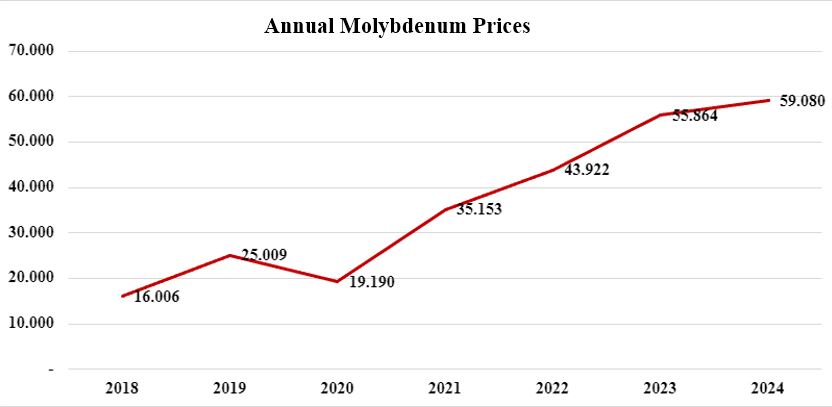
The lowest value in the world molybdic oxide market in the last 10 years was seen at approximately 6 US$/Ib at the end of 2015 and the beginning of 2016. It has continued its upward trend since mid-2020 (Figure 304). The average market value of molybdenum in 2022 is 43,600 US$/ton. The average for 2023 is approximately 56 thousand US$/ton. The average for the first ten months of 2024 is approximately 59 thousand US$/ton.
Date of Update: 26 December 2024
The details presented here have been prepared with the aim of informing the users of the website of our Ministry, and do not possess the characteristics of official binding documents.


